Chapter 1
License and support are, as we all know, crucial for the selection and operation of any system.
Numerous organizations that I am aware of are shelling out large sums of money for product licensing and support, but they are unaware of the true requirements and needs of these licenses, for which they are paying on an annual or monthly basis.
In addition to being legally required, licenses guarantee that we follow industry standards and safeguard our intellectual property.
By making the necessary license investments, we lower risks, protect our reputation, and enable our staff to provide the finest service possible to our clients.
It enables us to keep up the security and quality of our product by giving us access to vital support and upgrades.
So, I will show how to perform licensing of 3 Major Databases that is Oracle, MS SQL Server and IBM DB2.
We have 4 major Licensing models let discuss each one by one
and We should know each licensing model after that we can calculate actual requirement
Core Base
it's based on our computer or Server or Hardware Machine Processing unit capacity or no. of processing units used in our Harward machine or server machine.
and its commonly used in enterprise Level Environments Level Multinational firms, Bank, Industries like Mobile, Textile and Petroleum etc.
User Base
This model licenses the software based on the number of individual users who will access the system
It is often used when a company has a defined number of users, making it a cost-effective solution for organizations with controlled access needs.
This ensures that only authorized users can use the system, which helps in managing costs and maintaining compliance
It's possible that some organizations using expensive models that they don't require because they are unclear about which one they should use.
Subscription base
in subscription base model we don't need to buy license of this software we just need pay support cost on some agreed interval which may include maintenance and updates
during the agreed period.
Open Source
Last one in Open-Source Software which don't need any license cost or purchase cost even support is also as community support and experience on different stack holders.
so above models we can choose one the basis of our application criticality and decency on business model.
If we have 24x7 Application and we can't afford Down time for that types of system we should use that software which supports, updates and resources are easily available in the market.
Let’s begin by exploring the method for calculating requirements and needs for software product licensing.
This process involves assessing the necessary criteria and conditions to ensure that software licensing decisions are accurate, compliant, and tailored to the organization’s needs.
Our goal is to establish a clear and effective approach that supports optimal licensing strategies.
Physical cores
Physical cores are the individual, hardware components within a CPU (Central Processing Unit) that execute instructions, perform calculations and manage tasks. Each core operates independently,
allowing the processor to handle multiple operations simultaneously, which enhances overall performance. Physical cores directly manage data processing, run the operating system, and execute application tasks, making them critical to the efficiency and speed of a computer system.
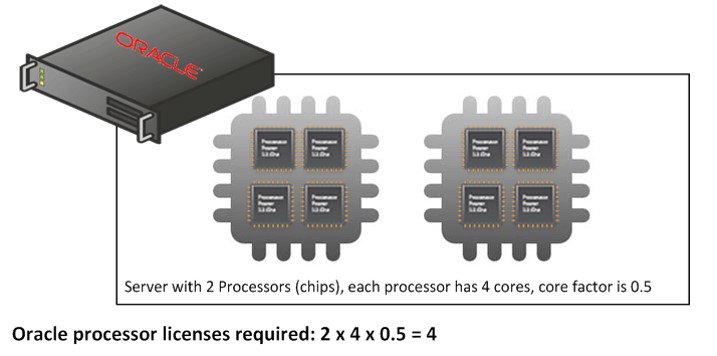
This picture shows two processors (or sockets or chips). Each processor has four cores. Therefore, there are eight physical cores in total.
Virtual Cores
Virtual cores, or virtual CPUs (vCPUs), are a concept used in virtualization. They represent the amount of processing power that a virtual machine (VM) has access to. In a virtualized environment, a physical CPU core is divided into multiple virtual cores to distribute processing power among different VMs.
Imagine you have a computer with a really powerful CPU. In a virtualized
environment, this CPU is split into several smaller pieces called virtual cores
or vCPUs. Think of it like slicing a big cake into smaller pieces so everyone at the party can have a piece.
Each virtual core represents a portion of the CPU's processing power that a virtual
machine (VM) can use. In This way, multiple VMs can share the same physical CPU,
each getting its own slice of the processing power to run smoothly.
So, virtual cores help us divide and share the CPU's power efficiently among different VMs!
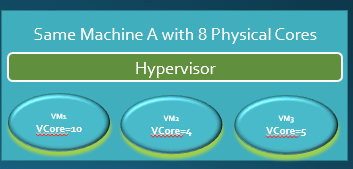
in this picture we have 8 cores physical machine in which we installed virtualization software like vmware or KVM then create 3 different virtual machines
VM1 has 10 Cores, VM 2 has 4 cores and VM 3 has 5 cores so each machine has different Cores so these are virtual cores
