
Oracle RAC (Real Application Clusters) is a database solution that enables multiple servers (nodes) to operate as a unified system, ensuring high availability, scalability, and improved performance. It allows the database to remain accessible even if one server fails, as the remaining nodes continue functioning seamlessly.
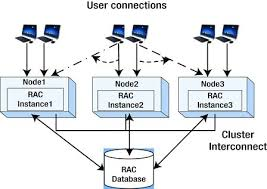
Key Components of Oracle RAC
Cluster Nodes
Physical or virtual servers that form the cluster. Each node runs an Oracle database instance, and all instances collaborate to access the same shared database, ensuring high availability and workload distribution.
Shared Storage
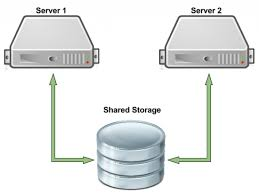
A centralized storage system (e.g., SAN or NAS) that is accessible to all nodes simultaneously. It houses the actual database files, ensuring data consistency and reliability across the cluster.
Clusterware
Oracle software responsible for managing the cluster, ensuring node coordination, failover handling, and cluster health monitoring. The primary component is Oracle Clusterware, which includes:
- Cluster Synchronization Services (CSS): Maintains synchronization between nodes and manages cluster membership.
- Cluster Ready Services (CRS): Oversees cluster resources, such as database instances and services, ensuring efficient operation and failover management.
Private Interconnect / Cluster Interconnect
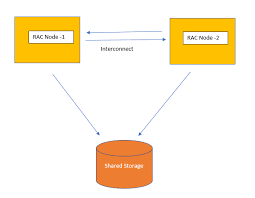
A dedicated, high-speed network that connects the nodes in the cluster. It facilitates communication and data sharing between nodes, ensuring coordination, consistency, and efficient workload distribution.
Oracle Database Instances
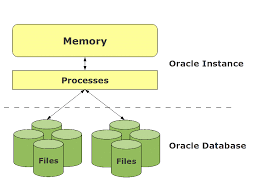
Each node in the cluster runs its own Oracle database instance, consisting of processes and memory structures. All instances operate together, accessing the same database stored on shared storage, ensuring high availability and scalability.
OCR (Oracle Cluster Registry):
A file stored on shared storage that contains configuration details for the cluster, including information about cluster resources, node assignments, and database instances. It ensures proper cluster management and resource coordination.
Voting Disk
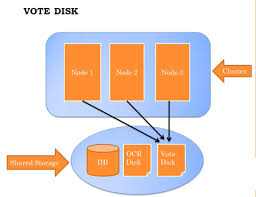
A special file stored on shared storage that manages cluster membership. It helps determine which nodes remain in the cluster during failures or network issues, preventing split-brain scenarios and ensuring cluster integrity.
Why Use Oracle RAC?
High Availability: Ensures continuous database access by allowing other nodes to take over if one server fails.
Scalability: Supports adding more servers (nodes) to accommodate growing workloads without downtime.
Load Balancing: Distributes database requests across all nodes, optimizing performance and preventing bottlenecks.
